EDI transactions are standardized electronic business documents used by trading partners to send and receive business information, such as when one company wants to electronically send a purchase order to another organization.
EDI transactions were designed to be standardized and are independent of the communications used by companies or the software technology that sends and receives the EDI data.
Use this guide to understand why EDI software is critical to the supply chain and learn every EDI transaction code by industry.
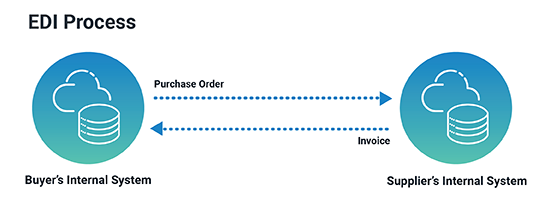
Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) is the computer-to-computer exchange of business documents between trading partners. EDI allows one company to send and receive information from another company electronically and in a standardized format, thereby enabling paperless communication. The EDI process replaces postal mail, fax, and email to connect directly to business systems.

EDI standards are the requirements for the format and composition of EDI documents. EDI standards delineate the correct order and location of units of data in a given EDI document.
All electronic data interchange transactions are made up of the following parts:
Element -The data elements within an EDI document are individual lines of information. For example, a document like a purchase order or an invoice, will contain data elements such as city, state, item number, or cost. Elements are the smallest component in an EDI standard.
Segments - Segments are composed of a group of elements. In an EDI document, each section of the document is described by a particular segment. Examples of segments include the beginning of a purchase order, the company, street addresses, etc.
Transaction Sets - Also referred to as an EDI message or EDI transactions. Once segments are collected in a predetermined format, they form the completed EDI document or transaction sets.
Electronic data interchange works depending on which EDI standards are required to format a message. Ultimately, since EDI documents are managed and interpreted by computers, transferred data must be formatted in a way that computers of both parties can understand. The main purpose of EDI standard formats is to minimize communication complications and costs of redundancies or fines, often called chargebacks.
Essentially, an EDI transaction is just another term for a standardized business document. Companies and trading partners exchange these documents using EDI standards to automate and streamline purchase orders, invoices, acknowledgments, payments, tracking, and other reports.
Any EDI transaction document must contain a certain minimum amount of vital data. Without these requirements, an EDI document becomes useless. Adhering to strict EDI feed formatting rules helps define precisely how and where each part of data on the document will be found and used. Each document is assigned one of the dozens of transaction numbers from the EDI public format.
For example, a purchase order (PO) is given the EDI transaction number 850 and the invoice transaction number is 810. So, when an EDI translator receives an EDI 850 PO document, it instantly recognizes the order number, the company name of the buyer, items in the order, and the price per item.
It’s these streamlined EDI transactions that improve the overall data transfer process through the efficient integration and seamless automation of B2B integration platform workflows between internal and external systems, applications, and cloud ecosystems.
Some of the biggest corporations in the world – industry-dominating giants – like Walmart mandate the use of some form of EDI format, meaning most companies must be EDI capable. Anything you purchase, any insurance document you file, any government form you report, any text message you send – it all requires EDI in some way, shape, or form.
Because there are hundreds of EDI transaction types, organizations follow designated EDI standards to ensure uniform formats for the inter-industry electronic exchange of business documents between trading partners.
Turn to Bay X Networks multichannel EDI and eCommerce solutions for affordable, reliable, easy to use, scalable cloud-based solutions. Bay X Networks cloud-based EDI and eCommerce portal, WebEDI, allows you to easily connect to trading partners, maintain 100% EDI compliance, integrate with your business systems and applications from shipping services, eCommerce solutions, accounting programs, to ERPs, 3PLs and more, achieve workflow automation and expand your business portfolio.
ANSI (American National Standards) ASC (Accredited Standards Committee) X12 goes by more than one pseudonym. This standard is also sometimes called ANSI X12 Standard or just simply X12. But regardless of the terminology, ANSI ASC X12 includes EDI standards used to communicate digital B2B transactions for various global business processes. EDI X12 standards allow consistency among business documents and other kinds of enterprise functionality.
There are more than 300 different types of X12 EDI standards, all delegated by a different three-digit number, for numerous industries such as finance, government, health care, insurance, transportation, and others. ANSI ASC X12 also develops standards for CICA (Context Inspired Component Architecture) and XML schemas.
TRADACOMS (TRAding DAA COMmunicationS) is the primary EDI standard for domestic trading in the United Kingdom, specifically the UK retail industry. While somewhat similar to the EDIFACT standard, TRADACOMS uses multi messages instead of relying on a format of single messaging. TRADACOMS communication is comprised of 26 messages structured in a hierarchy.
Each TRADACOMS message, much like EDIFACT, is given a six-letter application reference. For example, an invoice message is INVFIL, a payment order is PAYORD, a utility bill is UTLHDR, and so on.
UN/EDIFACT, which is short for United Nations rules for Electronic Data Interchange for Administration, Commerce, and Transport, is a set of internationally standardized communication guidelines for exchanged data tags and message types between computer systems in different networks. UN/EDIFACT standards structure data into segments, segments into messages, and messages into an interactive exchange protocol.
The syntax rules for EDIFACT describe the message (nesting, character sets, structures, etc.) The data tags detail the different types of data being exchanged and how each is represented. The message types are also known as UNSMs (United Nations Standard Messages).
ODETTE stands for Organization of Data Exchange by Tele Transmission in Europe and creates data exchange and communications standards for the European automotive industry. It is similar to North America’s AIAG (Automotive Industry Action Group). ODETTE develops protocols such as OFTP and the more advanced OFTP2, which provides enhanced security through encryption methods and digital certificates for EDI data exchange.
Deploying B2B and MFT (managed file transfer) solutions that are ODETTE-certified for OFTP and OFTP2 allows a company to securely and efficiently communicate with various software to successfully exchange data.
One of the most common complaints those in the technology world have had about EDI is due to its rigid standardization. However, this very same standardization has helped EDI stick around for as long as it has and become a way of life for enterprises. Without standardization, it becomes difficult to maintain and scale B2B data exchanges.
A lack of true EDI standards that dictate a universal format is one reason that APIs have not replaced EDI when it comes to B2B-type data exchanges. APIs can be customized to do just about anything, which means developers a pretty wide range of what he or she can do to meet the requirements of the business. Such wide-ranging business rules tend to not scale well in most organizations.
Every organization that needs to connect with trading partners must first ask themselves, “What is the best way to send and receive information and documents?” And while there are multiple avenues for a company to take business communication, data interchange ultimately comes down to AS2 vs. VAN.
With AS2 (applicability statement 2), data such as EDI, XML, and others are sent and received via the internet using an HTTP protocol (TCP/IP) through a certified server. AS2 offers a securely encrypted process without costly annual or transaction fees for unlimited data. In today's digital ecosystem, AS2 is considered the best way to integrate with trading partners and has been widely implemented across many industries.
AS2 can handle any type of file format and requires message disposition/delivery notifications (MNDs) to alert a trading partner when a document or data has been delivered or received. AS2 also can be deployed using in-house IT resources or outsourced through a cloud-based vendor.
With AS2, what it all comes down to is enabling a better way to send data securely and directly from one source to another.
An EDI VAN (value-added network) should efficiently deliver EDI transactions through a single connection. A hosted VAN service enables the communication between a traditional VAN and a private network or internet-connected trading partner. Simply put, a VAN is a communication channel that moves and manages data from point A to point B – kind like a post office. In a VAN, trading partners each possess a mailbox as data is delivered between each mailbox.
This streamlined method is meant to lower the document-by-document processing costs by way of a centralized system with real-time tracking, communication management, multiple connectivity options, local data integration, and rapid message delivery. However, relying on a VAN has become an outdated way of doing business, especially with more modernized and cost-effective technology options available that offer end-to-end connectivity and solutions to complex integration.
Acknowledgment – A response to a command that is sent to the originator to confirm the message was received. There are different types of EDI acknowledgments, ranging from basic-communication level statuses to functional acknowledgment. A functional acknowledgment is a message sent from the receiver of a transmission to the sender to indicate that the message was accepted.
Advanced Shipping Notice – A common EDI transaction, an ASN is a notification of a pending delivery, its primary purpose is to provide tracking and packing information ahead of delivery. Some of the most common elements included in an ASN are purchase order number, ship notice number, and the location where the product will be shipped.
Invoice – An electronic version of a document that a vendor sends to a buyer indicating how much is owed for goods and/or services. Usually, it is sent in response to a purchase order, which is a request for payment once the goods or services have shipped. They typically contain shipping details, payment terms, information on the goods, and/or services.
RESTful Web Services – Representational State Transfer specifies constraints that when applied to a Web service improve performance. As APIs become more common, REST architectures are useful because they allow data to be transmitted over a standardized interface, such as HTTP. They are stateless, and often are compared to Simple Object Access Protocol (SOAP), but are viewed as a simpler alternative.
Translation – Common in EDI, translation is the process by which information is converted into different formats. The receiving computer has a translator that knows where to find the buyer’s company name, order number, purchase items, and price, among other things. After that, the information is delivered to the receivers’ order entry to eliminate any manual order entry and expedite the transaction.
We help you see the world differently, discover opportunities you may never have imagined.